
RFID and Smart Tags: Transforming Business Management
The RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology is revolutionizing business management and redefining how companies optimize processes and ensure security. From real-time inventories to complete asset control, this technology offers unlimited opportunities. Want to know how implementing RFID can transform your business? Keep reading to find out.
What are RFID Tags and How Do They Work?
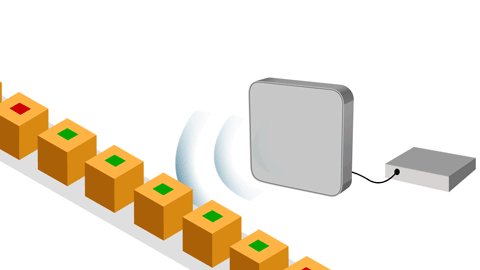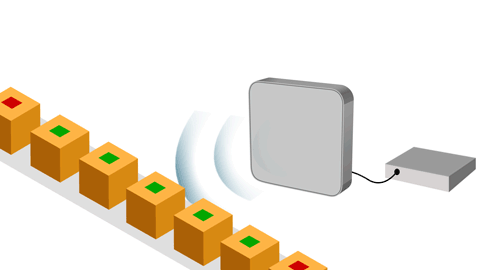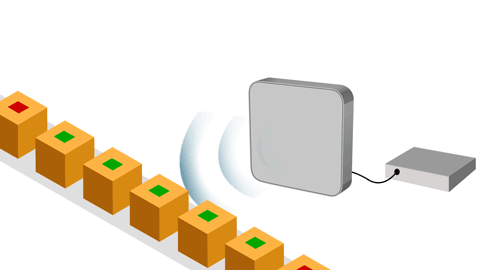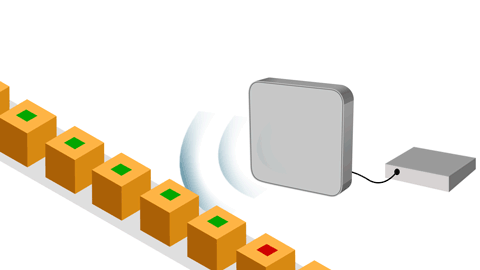
RFID tags, also known as RFID labels, are the essential components of radio frequency identification systems. These tags store unique data that allows objects, products, or assets to be identified and tracked in real time. They are designed to fit different needs and can vary in size, materials, and technical capabilities. There are two main types of RFID tags:
Passive RFID Tags:
-
They do not have their own power source.
-
They receive power from the RFID reader through radio waves.
-
They are ideal for low-cost applications such as inventories, traceability, and access control.
-
Example of use: Monitoring goods in a warehouse.
 Passive Tag | Kyubi System
Passive Tag | Kyubi System
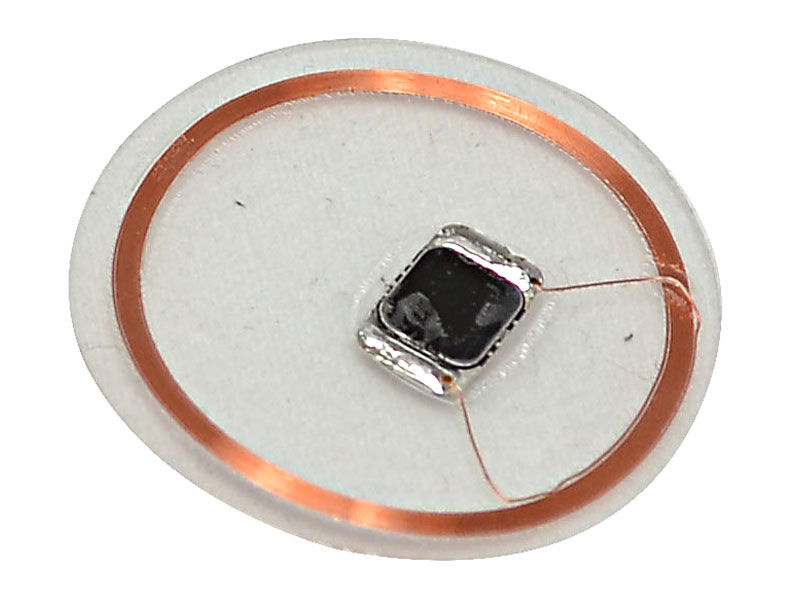
Active RFID Tags:
-
They have an internal battery to emit signals continuously or at scheduled intervals.
-
They offer greater range and storage capacity.
-
They are perfect for tracking high-value assets or monitoring real-time conditions.
-
Example of use: Monitoring temperature in the cold chain.
 Active Tag | Kyubi System
Active Tag | Kyubi System
Types of RFID Tags According to Their Design and Use
RFID tags are classified based on their design, materials, and specific applications:
-
Adhesive Labels:
Designed to stick to products or packaging. They are lightweight, cost-effective, and widely used in retail and logistics. -
Durable Labels:
Made from resistant materials like plastics or metals. They are ideal for industrial environments and extreme conditions. -
Micro Tags:
Ultra-small in size, used in products such as medications, jewelry, or electronic components where space is limited. -
Rewritable Labels:
Allow updating or modifying stored data multiple times, making them useful for dynamic applications. -
Sensor Labels:
Equipped with additional sensors to monitor variables such as temperature, humidity, or pressure, ideal for the food or pharmaceutical industries.
Operating Frequencies of RFID Tags
Depending on the frequency they operate on, RFID tags have different characteristics and applications:
Low Frequency (LF):
-
Range: 30 kHz – 300 kHz.
-
Advantages: High accuracy in readings at short distances and resistance to interference.
-
Applications: Access control and animal tracking.
High Frequency (HF):
-
Range: 3 MHz – 30 MHz.
-
Advantages: Higher reading speed and storage capacity.
-
Applications: Smart cards, libraries, and electronic payments.
Ultra High Frequency (UHF):
-
Range: 300 MHz – 3 GHz.
-
Advantages: Wider range and ability to read multiple tags simultaneously.
-
Applications: Large-scale inventories and logistics.
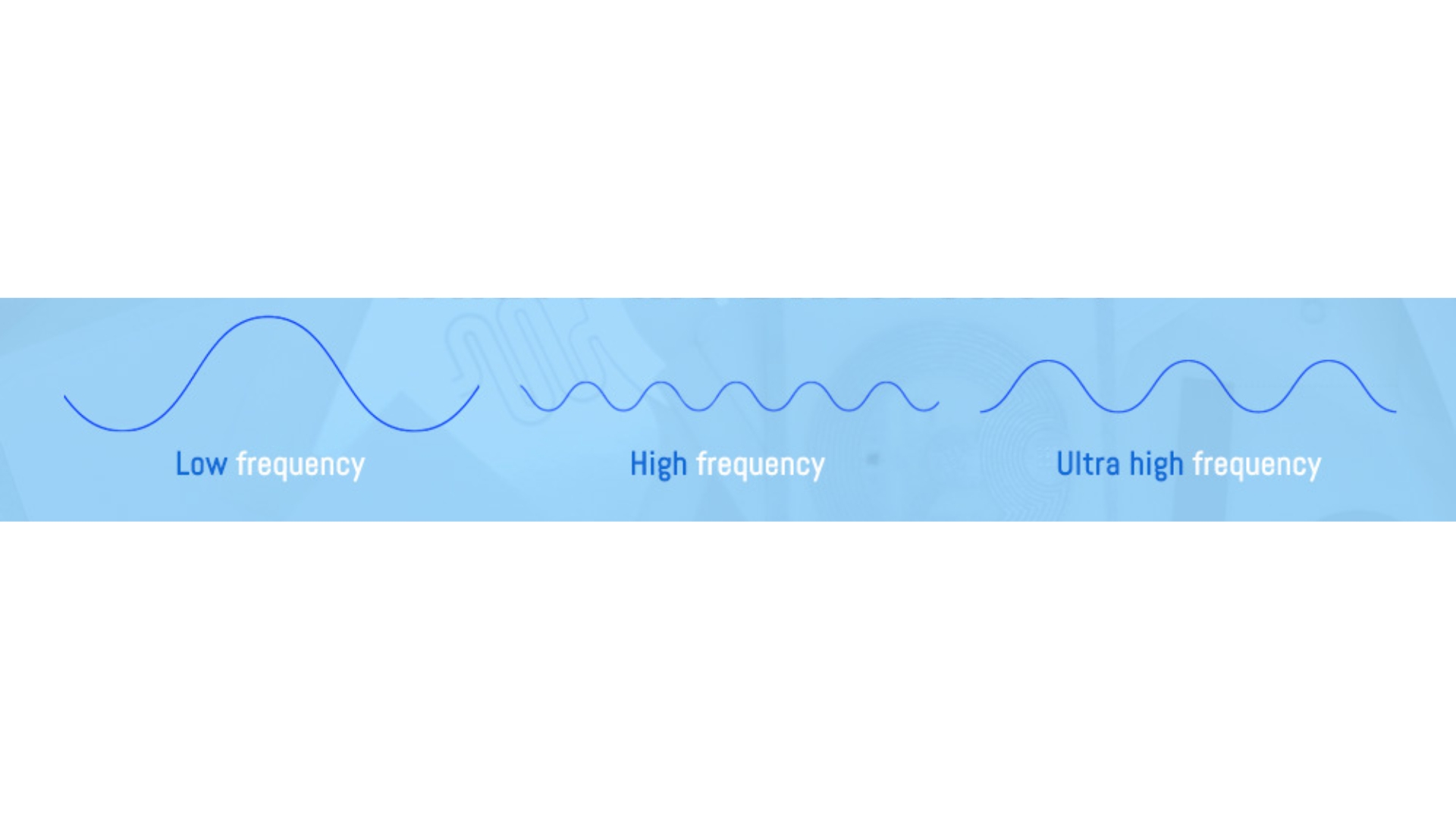 Frequency Differences
Frequency Differences
Why are RFID Tags Essential?
RFID tags are the backbone of advanced identification systems. Their ability to store and transmit data efficiently makes them an indispensable tool for:
-
Process Automation:
They simplify tasks such as inventory, asset control, and workflow management. -
Error Reduction:
They eliminate the need for manual intervention, reducing errors in data entry and tracking. -
Enhanced Security:
They guarantee product authenticity and prevent theft or counterfeiting with unique tracking systems. -
Resource Optimization:
They improve operational efficiency by providing real-time data on asset status and location.
 Process Automation
Process Automation
Key Applications of RFID Tags
-
Retail:
Inventory monitoring, loss reduction, and improved customer experience. -
Logistics and Transport:
Shipment tracking, route optimization, and real-time delivery control. -
Healthcare:
Medication monitoring, medical equipment control, and tracking of biological samples. -
Automotive Industry:
Parts management, vehicle tracking in production, and improvement of spare parts delivery. -
Cold Chain:
Ensuring that temperature-sensitive food or medicine maintains proper conditions during transport.
 Our Solutions
Our Solutions



